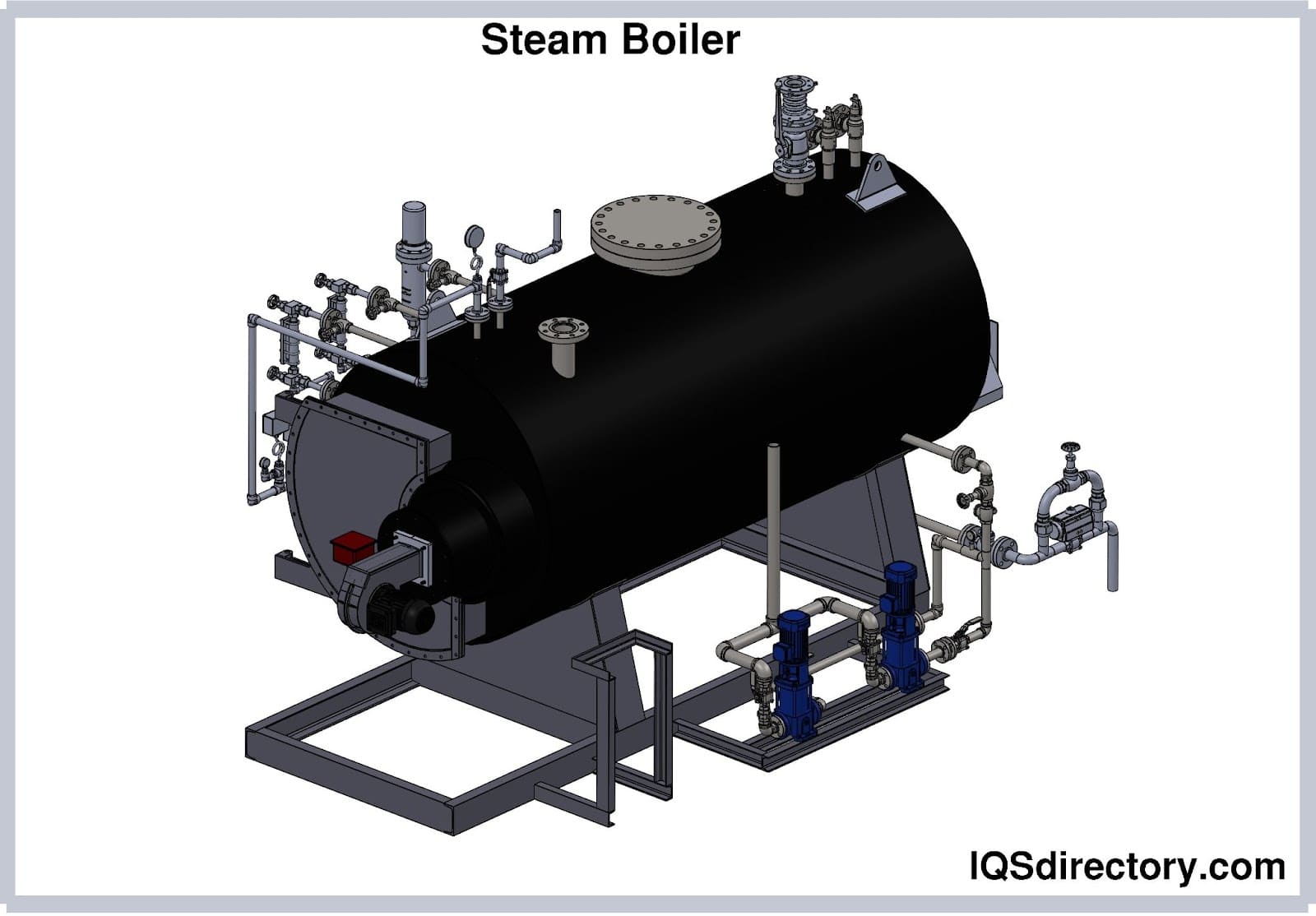
Boilers are machines that generate hot water, warm hair and heated steam for all industrial, commercial, domestic and residential settings. Industrial boilers are specifically made to use as parts of larger heating systems, or to provide steam or hot water for industrial and manufacturing processes. Read More…
We strive for the best at Unilux Advanced Manufacturing LLC. Our boilers are designed with superior materials. We are proud to say that we produced the world's first UL/FE boiler and our units provide the highest levels of safety and accountability.

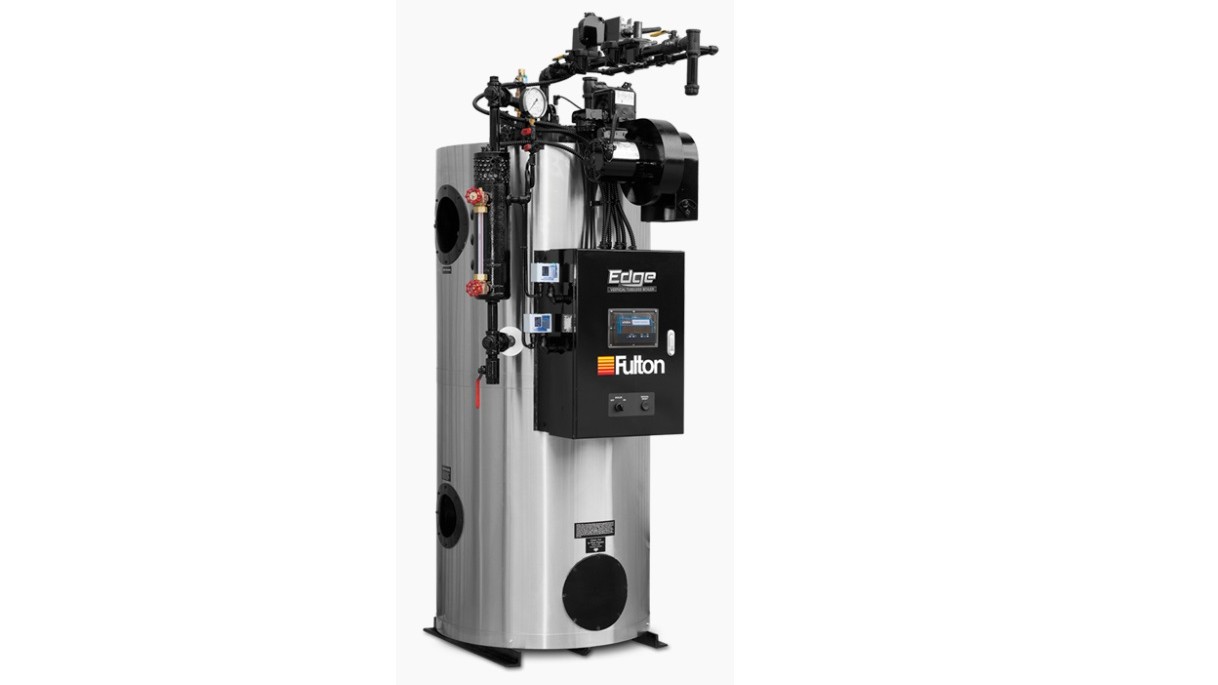
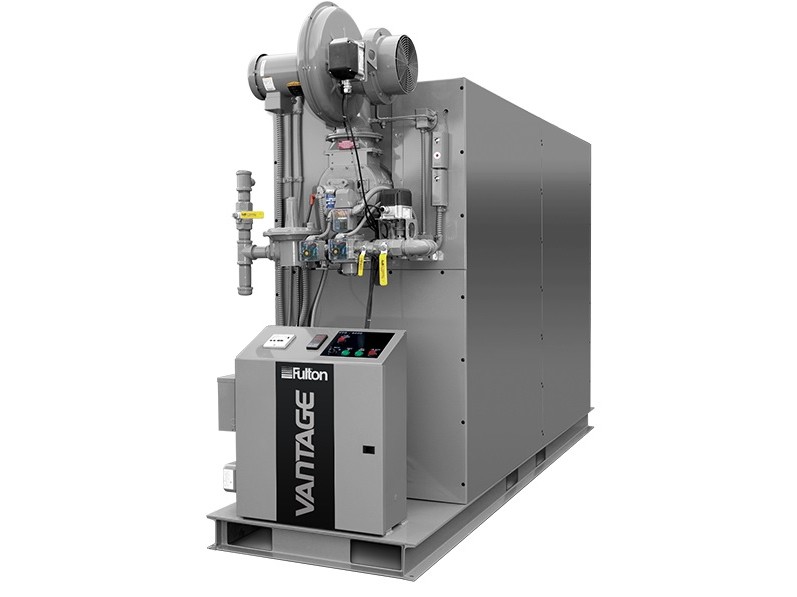
As the inventor of the vertical tubeless boiler, Fulton has a reputation for success dating back to 1949. We`re a global manufacturer of steam, hot water and hydronic boilers, thermal fluid heaters, and custom engineered systems.

Miura Boiler Co., Ltd. has been manufacturing, designing, engineering and servicing gas, oil, coal, wood, solid waste, biomass & hybrid fuel-fired steam & gas and condensing since our inception. With installations across all industries worldwide, We are recognized for the highest code standards, innovative engineering and design, Energy Star rating, fully Integrated controls, and renewable,...
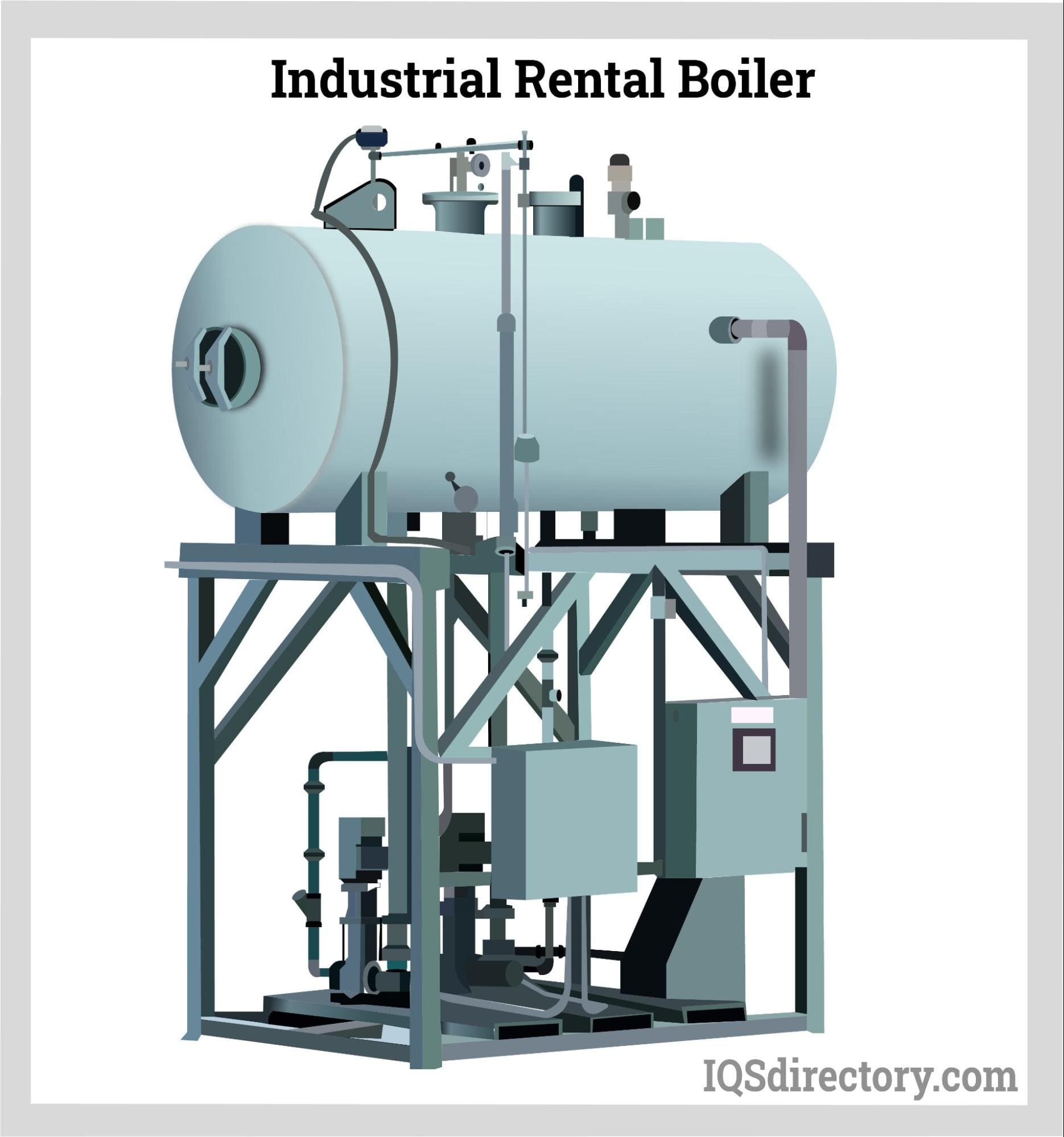
Indeck has the largest inventory of steam generating systems, a custom boiler design team and our own boiler manufacturing plant . Indeck is the complete steam power solution provider with emergency rental of 25,000 pph trailer-mounted rental boilers to the design of large custom million pound boilers. Our expertise includes watertube, mobile, packaged, waste heat, solid fuel, biomass and fire...
Bryan Steam has been an industry leading producer of commercial boilers, including their “flexible water tube” model for more than one hundred years. Bryan Steam produces a wide range of gas, oil, dual fuel and electric water and steam options including the ultra-high efficiency Free-Flex models 1000 MBH to 6000 MBH and the BFIT model 1000 MBH to 4000 MBH. Contact the company today for...

At Mid-South Steam Boiler & Engineering Co., we are dedicated to providing top-notch boiler solutions and engineering services tailored to meet the needs of our diverse clientele. With a rich history spanning several decades, we have established ourselves as a trusted authority in the boiler industry, renowned for our commitment to quality, reliability, and customer satisfaction. Our product...
Nationwide Boiler is a leading supplier of new and reconditioned boilers for industrial facilities worldwide. We’re a manufacturer’s representative and stocking distributor for B&W package watertube boilers and Superior package firetube boilers, and we have fully reconditioned boilers in a variety of types and sizes. With sales, service and equipment depots throughout the U.S., we strive to...

More Industrial Boiler Manufacturers
Industrial Boiler Applications
Industrial boilers serve as the backbone of numerous systems and applications, supplying heat and power for steam generation, agricultural soil steaming, turbine operation, cement production, and kiln heating, among other uses.
These versatile boilers are integral to industries such as manufacturing, electrical, paper and pulp, agriculture, metalworking, ceramics, refining, and food and beverage, supporting a diverse range of industrial activities.
History of Industrial Boilers
Boilers trace their origins to the late eighteenth and early nineteenth centuries when the dawn of the steam age began. In these early days, people started using steam boilers on a modest scale. They employed kettle-type boilers, which featured a firebox. Water was placed above the firebox, where it was heated until it transformed into steam.
In 1867, this straightforward model evolved into the convection boiler. While there is some debate over the true originator of this invention, it’s clear that Steven Wilcox and George Babcock were the first to secure a patent for the design. These pioneering figures later established the influential Babcock & Wilcox Company in New York City in 1891. The initial boilers produced by their company were modest in size, featuring firebrick walls to enhance combustion. These early models required manual feeding with lump coal and operated at relatively low temperatures.
In parallel, Ohio’s Stirling Boiler Company manufactured robust industrial steam boilers. Their standout creation, the H-type boiler, surpassed competitors in size, boasting a design with bricks and three drums facilitating efficient water and steam circulation. In 1907, after sixteen years, Babcock & Wilcox merged with Stirling Boiler, rebranding the H-type boiler as the H-type Stirling, sparking widespread acclaim. This iteration of the H-boiler could produce an impressive 50,000 pounds of steam per hour. In 1912, rivals American Stoker and the Grieve Grate Company innovated boilers equipped with screw-type or traveling grates at the base, facilitating the even distribution of lump coal along the boiler’s length. Additionally, they incorporated a hopper to gather ash and surplus fuel. Eventually, these competitors merged, christening their collaborative boiler the Type E.
As companies vied for dominance, they effectively made boilers more accessible and attractive. Yet, as industrial boilers grew in size and heat intensity, they faced mounting challenges with overheating hazards. Engineers responded by scaling up boiler sizes to regulate pressure and temperature more effectively. However, this approach proved highly inefficient and impractical. The breakthrough came in the 1920s with the invention of the tube and tile boiler, which replaced bulky firebrick walls with thin, insulated tile walls. This innovation not only enhanced safety but also greatly improved efficiency.
During the late 19th and early 20th centuries, an alarming toll of 50,000 lives per year in North America was attributed to boiler-related accidents. The mentioned reforms, alongside the establishment of safety organizations such as ASME, significantly mitigated the hazards associated with boilers.
During this era, the boiler industry surged ahead, swiftly diversifying its offerings to include a plethora of types: from two-drum and vertical two-drum boilers to flat studded tube and loose tube wall boilers. Innovations like the latter two, emerging in the 1920s and 1930s, facilitated the transition from lump coal to pulverized coal for boiler users. By the 1940s and 1950s, boilers gained widespread popularity among large institutions requiring heating, such as universities, hospitals, manufacturing plants, and government offices. This demand spurred manufacturers to produce both bespoke and prefabricated boiler solutions.
Since the 1970s and 1980s, there has been a notable shift in consumer priorities towards sustainability and reduced emissions. Legislative measures, such as the Public Utility Regulatory Policies Act of 1978, prompted manufacturers to transition from coal to alternative energy sources, primarily electricity. Following this initial transition in the late 1970s, manufacturers began innovating with various alternative fuel boilers, including biomass and fluidized bed boilers. Today, engineers and boiler manufacturers remain committed to advancing cleaner and more efficient energy technologies.
Boilers have endured a tumultuous history; initially, the unclear relationship between temperature and pressure led to significant dangers, prompting calls for their abandonment. With advancements in materials, design, and construction techniques, modern boilers rarely pose safety risks. Today, they serve crucial roles across diverse settings, from factories to schools. As technology progresses, boilers continue to shrink in size, fitting into increasingly compact spaces. Remarkably, portable heaters now empower emergency crews, military personnel, and individuals in transitional environments with efficient heat and power solutions.
How Industrial Boilers Work
Industrial boilers typically derive their energy from one of three primary fuel sources: gas, oil, or electricity. Additionally, some, like central boilers, operate on wood as fuel.
The operation of boilers hinges on the transmission of radiant heat and thermal energy, directing the flow of water or steam. As heat naturally migrates from warmer to cooler regions, a furnace can heat the tubes that warm the water, subsequently heating pipes or radiators that then warm the space. Thus, the boiler’s function revolves around the behavior of high-temperature fluids.
Types of Industrial Boilers
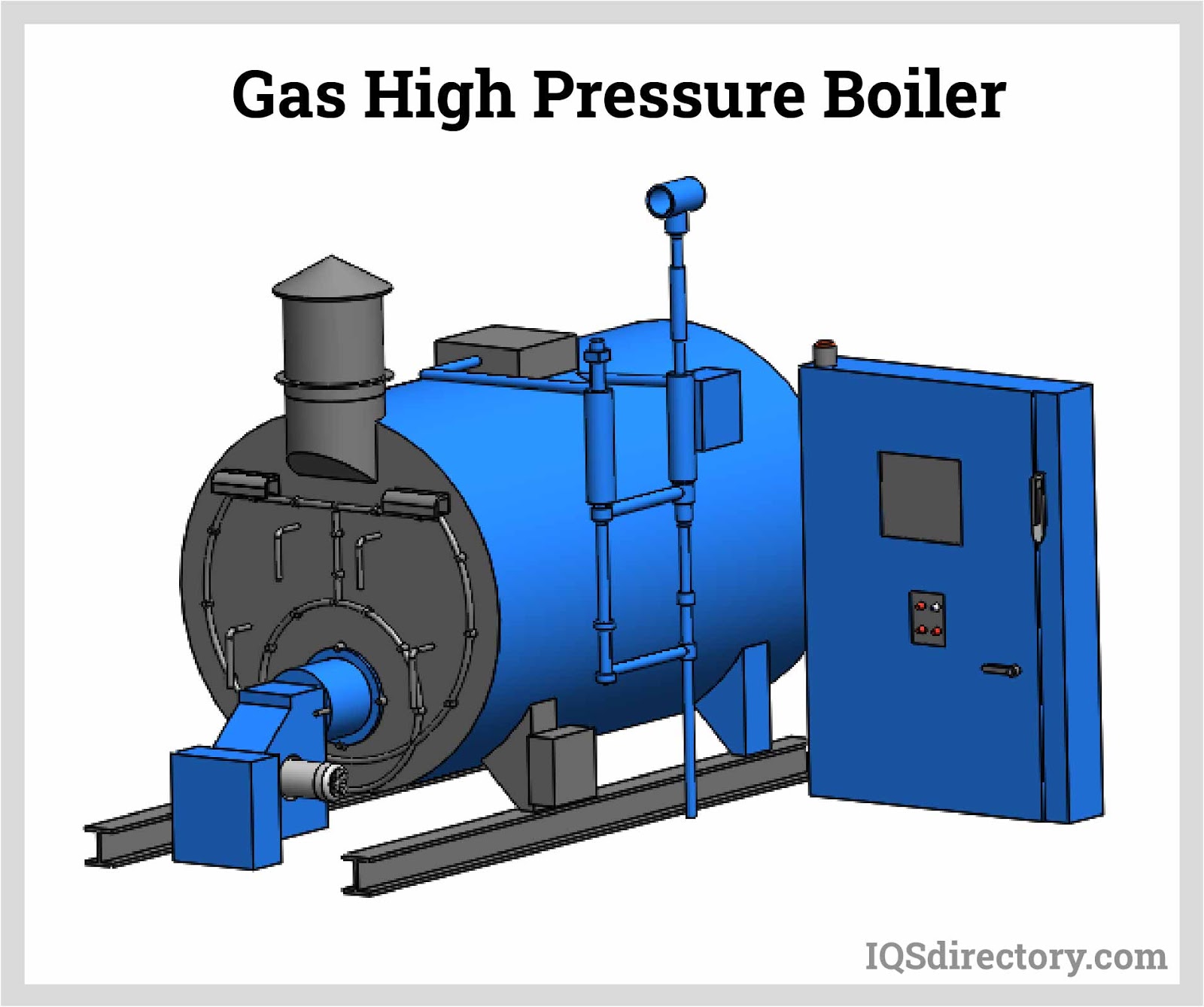
Gas Boilers
Gas boilers, the predominant type found in the USA, generate steam by heating water to a precise temperature or boiling point using a natural gas flame. These boilers play a crucial role for several reasons. Firstly, they supply heat and energy to large structures such as warehouses and industrial facilities. Additionally, they heat water that flows through piping systems, supporting radiators, baseboards, and other heat exchange mechanisms.
Oil Boilers
Oil boilers generate hot gasses using oil. These gasses serve dual roles: they either fuel furnaces or substitute the water typically used in boilers.
Fire Boilers
Fire boilers, or fire-tube boilers, are boilers that use hot gasses generated by fire. To make this boiler work, the gasses pass through one or more tubes inside a sealed chamber of water. Once there, the gasses heat the tube walls via thermal conduction and heat the water in order to create steam. Simply put, fire-tube boilers distribute heat through tubes immersed in water.
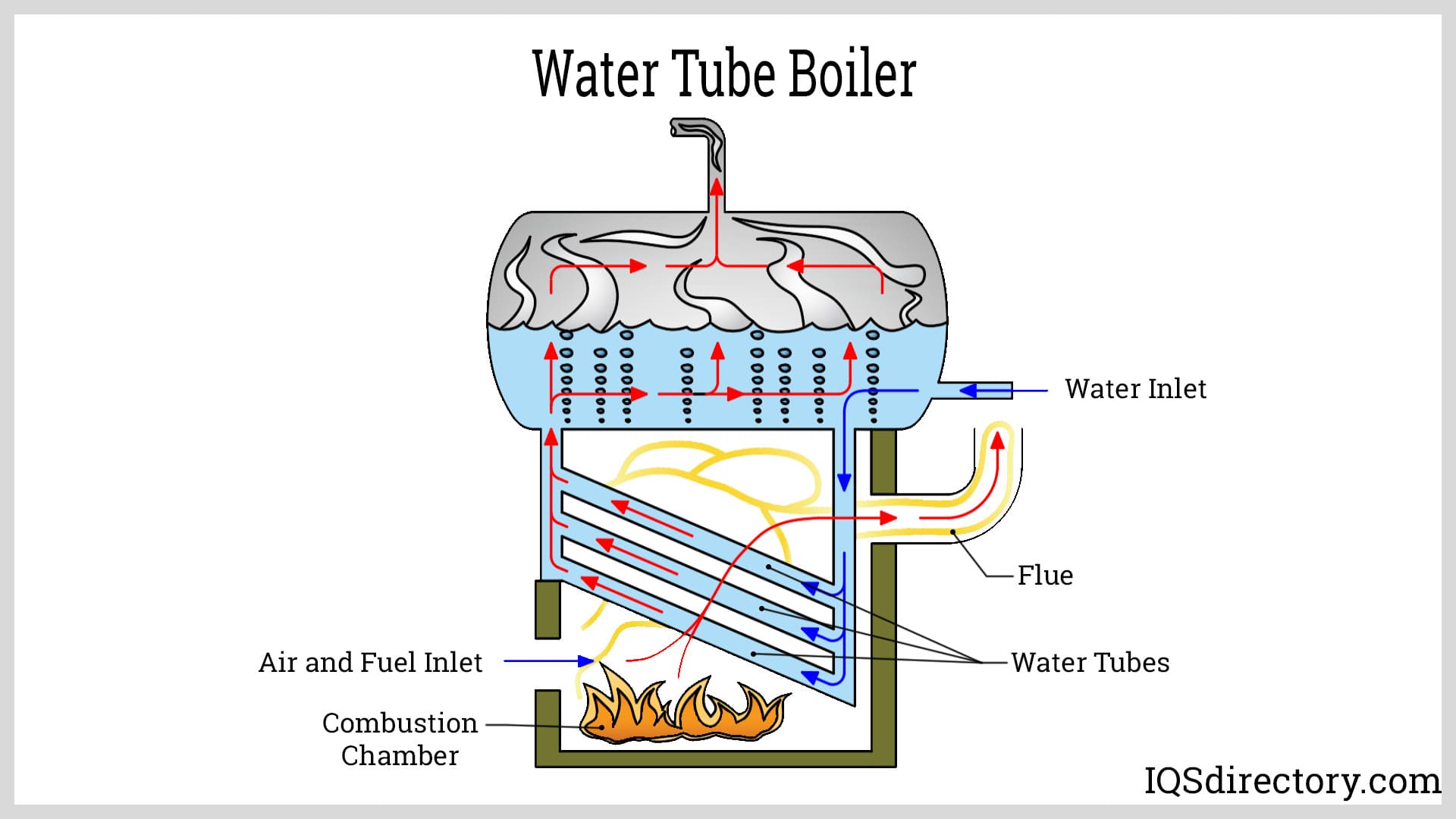
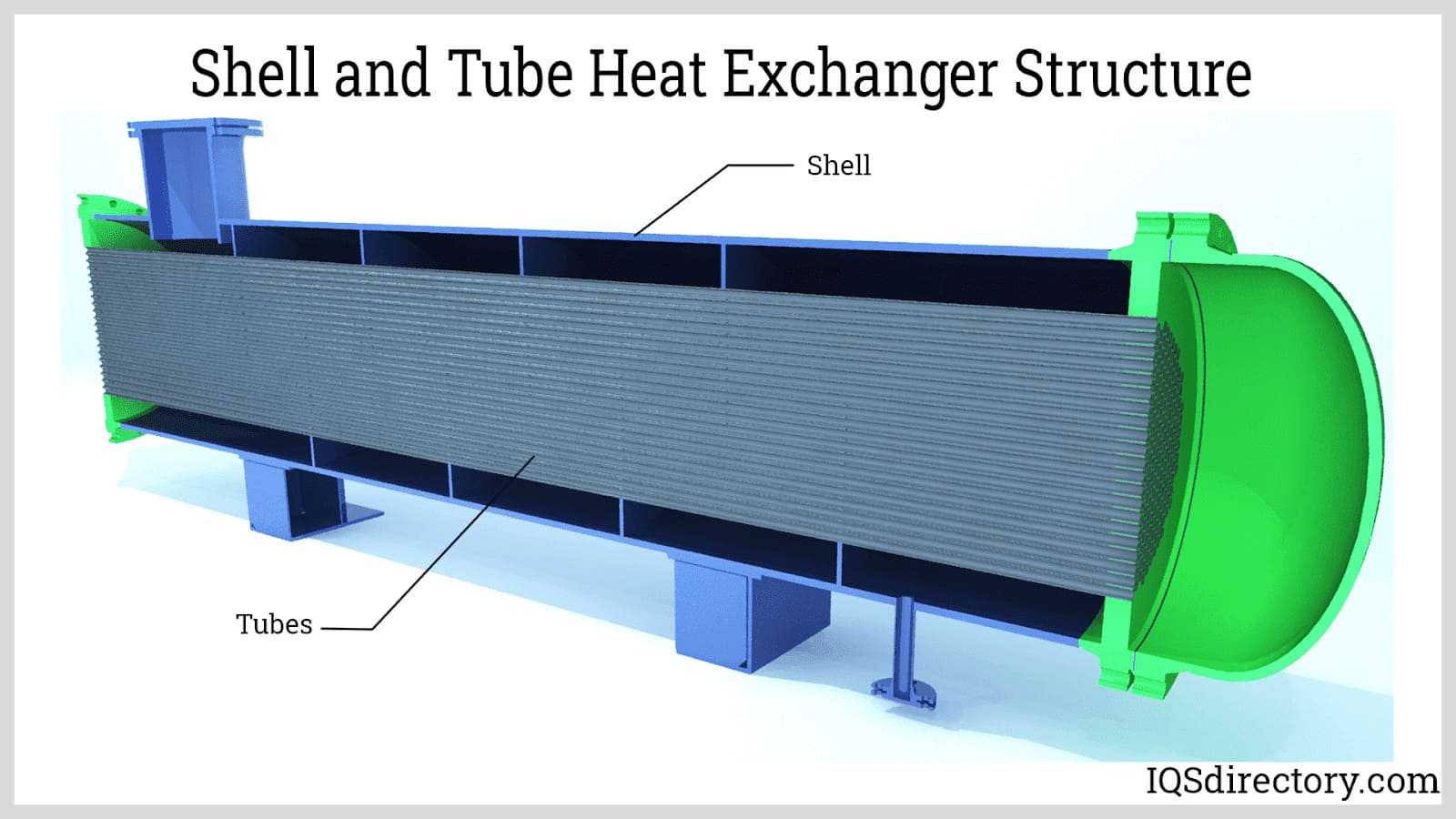
Water Tube Boilers
Water tube boilers utilize a configuration where water-filled tubes are housed within furnaces. This design enables the distribution of water through heated tubes within an enclosed structure. As hot flue gasses pass over these tubes, they first heat the water before exiting through a stack. These boilers can employ various heat sources and operate independently or in conjunction with large upper and lower drums. In such setups, upper drums store water and steam, while lower drums contain water exclusively. Alternatively, water tube boilers can integrate pumps and coils to circulate water, facilitating high steam production. Boilers configured in this manner are referred to as mono-tube boilers. Generally, water tube boilers are preferred for applications requiring high pressures.
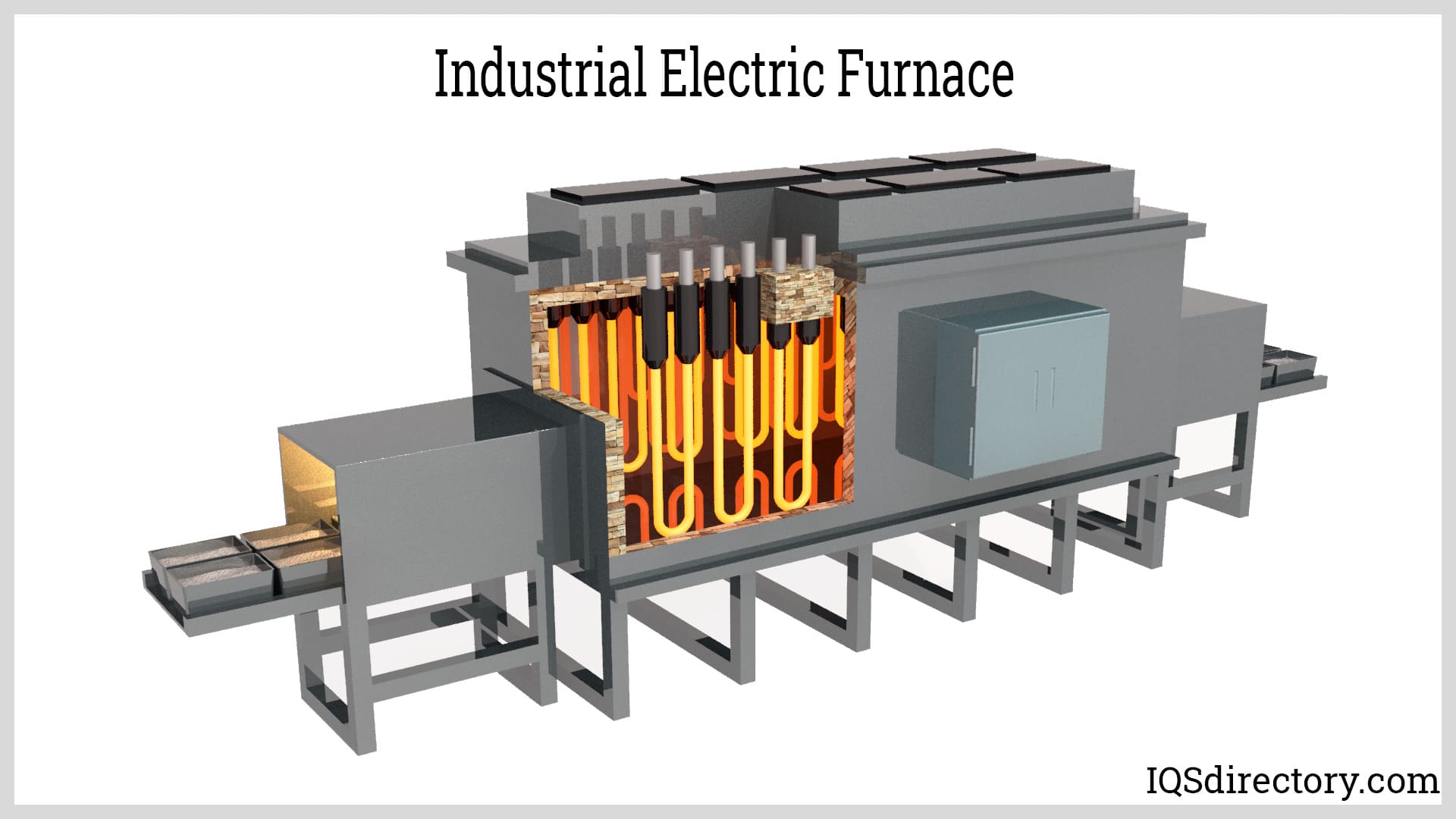
Electric Boilers
Electric boilers harness electricity to efficiently, cleanly, and safely heat water. This method is favored for its absence of combustion elements, eliminating concerns related to pilot lights, gas piping, venting, or carbon monoxide.
High Efficiency Boilers
High-efficiency boilers operate at significantly elevated pressures, reaching levels as extreme as 1,000 PSI.
Low Efficiency Boilers
Low efficiency boilers, operating at pressures below 15 PSI, are typically employed in smaller buildings or for heating individual spaces.
Waste Heat Boilers
Waste heat boilers, often referred to as waste heat recovery units (WHRU), are specialized boilers designed to harness energy from sources rich in potential heat (such as steam, hot flue gas, or waste water). By capturing and utilizing this otherwise wasted energy, they effectively recycle it as fuel. This approach not only enhances efficiency but also aligns with eco-friendly practices, distinguishing them favorably from conventional boilers. Waste heat boilers find widespread application, particularly in industries like pulp and paper manufacturing.
Biomass Boilers
Biomass boilers combust wood and various organic materials as fuel. They offer a more environmentally favorable option compared to fossil fuel-burning counterparts since the carbon released from biomass is part of the natural carbon cycle. In contrast, fossil fuels introduce carbon into the atmosphere that has been sequestered for millions of years. Despite these benefits, biomass boilers still emit pollutants into the environment.
Industrial Boiler Equipment Components
Boilers typically include several key components: a combustion system (utilizing oil, gas, coal, electricity, biomass, etc.), along with tubes and enclosures for containing water or steam. Depending on their configuration, boilers may incorporate additional elements like safety valves, pressure gauges, water level indicators, check valves, low-water alarms, stop valves, fusible plugs, and more.
Industrial Boiler Design and Customization
In the process of designing boilers, manufacturers take into account various factors such as system size, heat demands, specific industry/application needs and constraints, desired efficiency, sustainability goals, environmental considerations, and available installation space.
They weigh these factors and determine specifics such as boiler type, combustion technology, configuration, size, and material. Industrial boilers are usually constructed from durable materials such as stainless steel, cast iron, and aluminum to enhance longevity, safety, and efficiency. Suppliers offer customization options such as tailored controls, specialized certifications, enhanced accessibility, improved shock resistance, bespoke dimensions, and personalized nameplates to meet unique requirements.
Industrial Boiler Safety and Compliance Standards
Boiler safety and compliance standards are well-established, particularly in the United States where the ASME (American Society of Mechanical Engineers) sets prominent benchmarks. The ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code offers a comprehensive framework of rules and recommendations. It is crucial to ensure that your industrial boiler manufacturer adheres to ASME standards when constructing your boiler. Additionally, compliance with EPA (Environmental Protection Agency) standards is essential. In Europe, significant codes include EN standards and British BS codes. Depending on your industry and application, your boiler may also need to meet specific standards such as those set by the FDA. For detailed guidance, consulting with colleagues, industry experts, or relevant governmental bodies is recommended.
Things to Consider Regarding Industrial Boilers
Boilers must endure intense and variable temperatures and pressures to consistently deliver heat to various points. Utilizing tubes, they facilitate indirect heat exchange from combustion gasses to water, generating steam or elevated-temperature water. Over time, their efficiency diminishes due to scale accumulation and other deteriorative factors. It’s advisable to conduct annual boiler inspections to enhance efficiency and prevent costly downtime. Delaying maintenance until breakdown occurs can lead to operational interruptions and substantial expenses for boiler replacement. Moreover, regular inspections can detect potential tube failures early, enabling prompt retubing that significantly prolongs the boiler’s lifespan.
If you seek an industrial boiler, we strongly advise collaborating with a reputable custom boiler manufacturer. Not all companies are alike, so to ensure a reliable partnership, we’ve curated profiles of top industry leaders for your consideration. As you review them, remember that the ideal manufacturer isn’t necessarily the cheapest, but rather the one that excels in customer service and provides the most suitable machinery for your needs.
Check out our Flow Meters website


 Boilers
Boilers Chillers
Chillers Cooling Towers
Cooling Towers Furnaces
Furnaces Heat Exchangers
Heat Exchangers Heat Transfer Equipment
Heat Transfer Equipment Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services